The rook is one of the six different types of chess pieces and is one of the original pieces that has been in use since the earliest forms of the game. It is also sometimes referred to as a castle, represented as a fortified tower.
The origins of the rook are somewhat uncertain, but it is believed to have evolved from the chariot or war wagon, which was a powerful military vehicle used in ancient times. The chariot had a similar movement pattern to the modern-day rook, as it could move in a straight line horizontally or vertically.
As chess evolved from its early forms in India, Persia, and Arabia, the rook gradually became a more important and powerful piece on the board. In medieval Europe, the rook was often depicted as a castle or tower, which is where its alternative names come from.
Today, the rook is a fundamental piece in the game of chess, and its unique movement pattern allows it to control open lines and attack enemy pieces from a distance. It is often used in conjunction with other pieces, such as the queen, to launch powerful attacks against the opponent.
How Does The Castle Move?
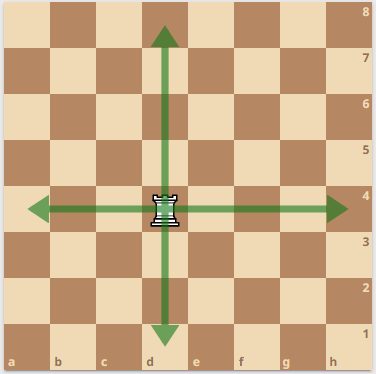
The castle, popularly known as the rook can move and capture horizontally or vertically along a rank or file, as far as it wants to go until it reaches the edge of the board or another piece blocks its path.
To be more specific, the rook moves by sliding along any row or column that it is currently occupying, in any direction. The rook can move any number of squares along the same rank or file, as long as there are no pieces in the way.
The rook moves vertically or horizontally along the files or ranks of the chess board
In chess, the rook captures an opponent’s piece by moving to the square occupied by the opposing piece.
How Does The Rook Capture?
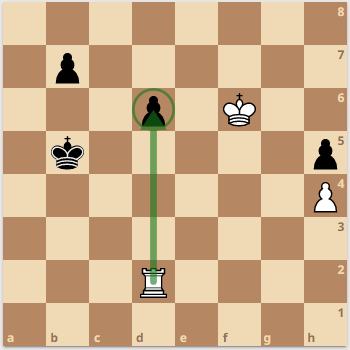
The rook captures using the same movement pattern as it does when it moves, that is, it can capture any piece that is in the path of its movement along a rank or file. For example, in the position below, the rook on d2 can capture black’s pawn on d6 along the d-file by moving vertically up the board.
Strategies Involving the Rook
The rook is a powerful piece in chess and has a number of strategic uses on the board. Here are some common strategies involving the rook (castle):
Occupy open lines
One of the main strengths of the rook is its ability to control open lines, especially when they are not blocked by pawns or other pieces. Placing your rook on an open file or rank can put pressure on your opponent’s pieces and restrict their mobility.
Support pawn advances
Rooks can be used to support pawn advances by protecting them as they move up the board. This can be especially useful when trying to create passed pawns, which can be a major attacking force in the endgame.
Coordinate with other pieces
The rook can be a powerful attacking force when coordinated with other pieces, such as the queen or other rook. For example, a rook and queen working together can create powerful threats against the opponent’s king and pieces.
Control the seventh rank
Placing a rook on the seventh rank (the second rank from the opponent’s side of the board) can be a powerful strategic move.
From this position, the rook can threaten pawns and pieces, support pawn advances, and create threats against the opponent’s king. Getting 2 rooks to the 7th rank is even more dangerous for your opponent and can sometimes lead to checkmate. This concept is sometimes referred to as pigs on the 7th rank because they can gobble up pawns along the rank.
Getting your rooks on the 7th ranks is a powerful strategy
Use in the endgame
In the endgame, rooks can be particularly effective in creating mating patterns and forcing the opponent to give up material. Two rooks can work together to create a mating net around the opponent’s king, while a rook and pawn can form a deadly threat to promote the pawn to a queen.
Overall, the rook is a versatile and powerful piece that can be used in a variety of strategic ways, depending on the position of the pieces and the overall goals of the game.
Castling With The Rook And King
Castling is a special move in chess that involves both the rook and king, with the purpose of safeguarding the king from attacks.
When castling in chess, the rook moves to a specific square on the board, depending on whether the player is castling kingside or queenside. Here’s how the rook moves when castling:
Kingside Castling
To castle kingside, the king moves two squares towards the rook on its starting square (either e1 for White or e8 for Black). The rook on the h-file (either h1 for White or h8 for Black) then moves to the square immediately to the left of the king (f1 for White or f8 for Black).
Before kingside castle

After kingside castle

Queenside Castling
To castle queenside, the king moves two squares towards the rook on its starting square (either e1 for White or e8 for Black). The rook on the a-file (either a1 for White or a8 for Black) then moves to the square immediately to the right of the king (d1 for White or d8 for Black).
Before queenside castle

After queenside castle

It’s important to note that in order to castle, there are a number of conditions that must be met. These include:
- The king and the rook must not have moved previously in the game.
- There must be no pieces between the king and the rook.
- The king cannot be in check or pass through a square that is attacked by an enemy piece.
- The king cannot end up in check after castling.
Castling is an important move in chess, as it allows the king to move to a safer position and bring the rook into play. The rook plays a key role in the castling maneuver, helping to create a defensive structure around the king and potentially opening up attacking opportunities on the opposite side of the board.
Final Thoughts
Because of the special move called castle, it is not wise to call the rook a castle as it may create confusion among beginner level players.
The rook is a highly important piece in chess, valued at 5 points, the same value as a minor piece (3 points) and 2 pawns combined. Its ability to move and control along ranks and files, occupy open lines, coordinate with other pieces, and control key areas of the board make it a powerful attacking and defensive force.
Overall, the rook is a versatile and essential piece in chess that can play a key role in determining the outcome of the game.


